APPLICATION CENTER
Rail Transit
Rail transit refers to a type of vehicle or transportation system that requires operating vehicles to travel on specific tracks. Rail transportation includes urban rail transportation such as subways, light rails, and trams, as well as railway transportation such as high-speed railways and ordinary-speed railways.

Steel for rail transit mainly includes steel for line paving, steel for vehicles, steel for infrastructure construction such as bridges, tunnels, and stations, and steel for electrified railways. There are many types of steel.
|
use |
Main steel varieties |
|
Line laying |
Mainly include steel rails (light rail and heavy rail) and its accessories (accessories include fishplates, backing plates, switch rails, gauge baffles, etc.), sleeper steel (modulated steel bars, fine-rolled rebars, high-strength bolts, and prestressed steel wires) Wait) |
|
Steel for vehicles |
Wheels, hubs, axles, penetrating bearing steel, spring steel, corrosion-resistant steel, weathering steel, cold-formed steel, H-beam steel, color-coated steel, stainless steel, etc. The steel used for railway freight cars is mainly high-strength atmospheric corrosion-resistant steel |
|
Steel for infrastructure |
Mainly rebar, wire rod, round steel, steel plate, etc. |
|
Steel for electrified railway |
H-beams, steel strands, weather-resistant steel and steel pipes of various sizes, etc. |
*Main varieties of rail transit line laying and vehicle steel
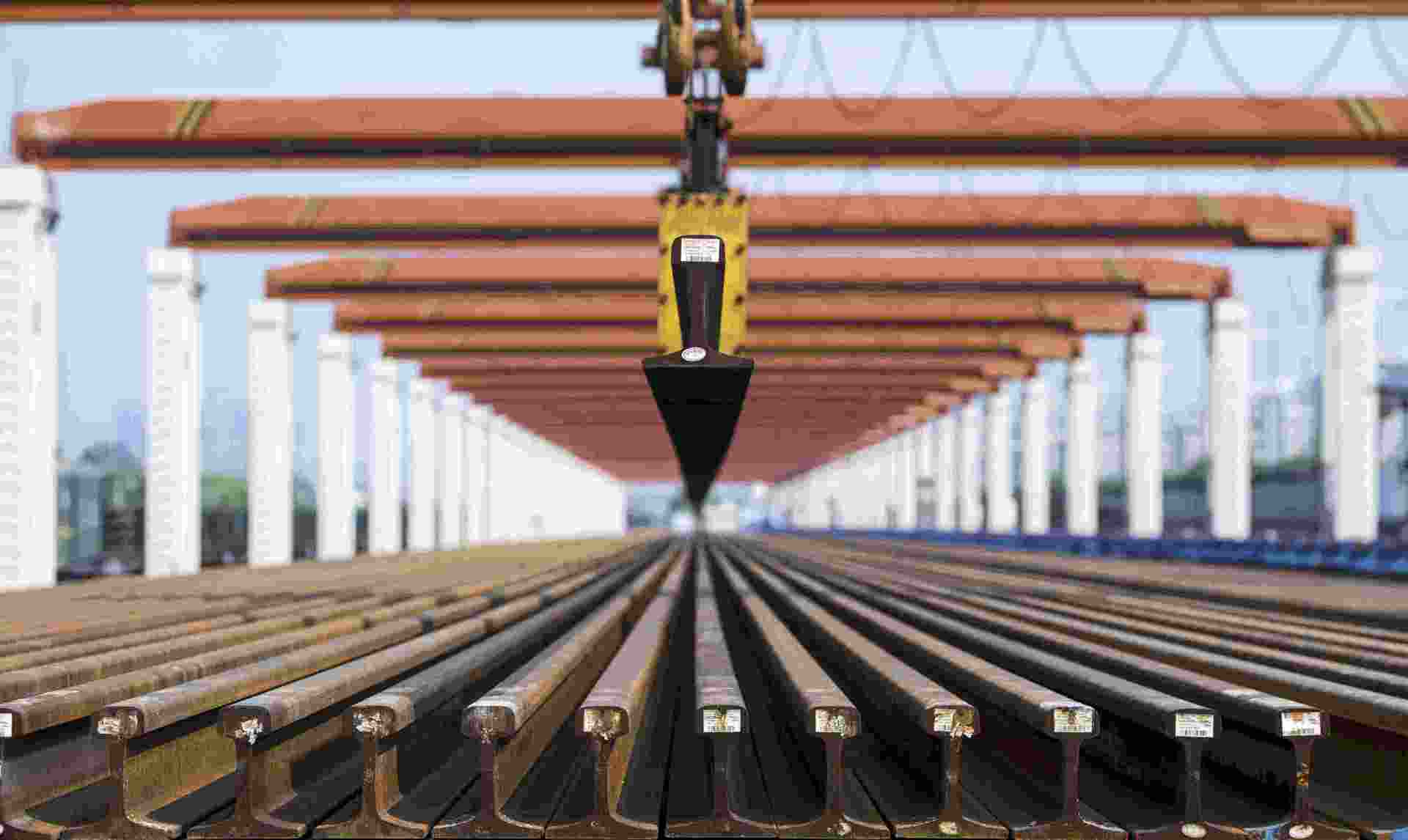
1. Steel rail The
rail directly bears the train and its load mass transmitted by the wheels, and guides the direction of the train. Compared with ordinary lines, passenger dedicated lines, high-speed trains and heavy-duty trains have extremely strict requirements on the safety of steel rails. Rails must not only withstand the pressure of locomotives and vehicles, but also withstand the impact load caused by high-speed trains. Therefore, the rails need to have sufficient strength, hardness, toughness and good welding performance. Rails are usually divided into heavy rails and light rails, and heavy rails include train rails and crane rails. Heavy-duty rails are steel rails with a nominal weight of more than 30kg per meter, and light rails are steel rails with a nominal weight of less than or equal to 30kg per meter.

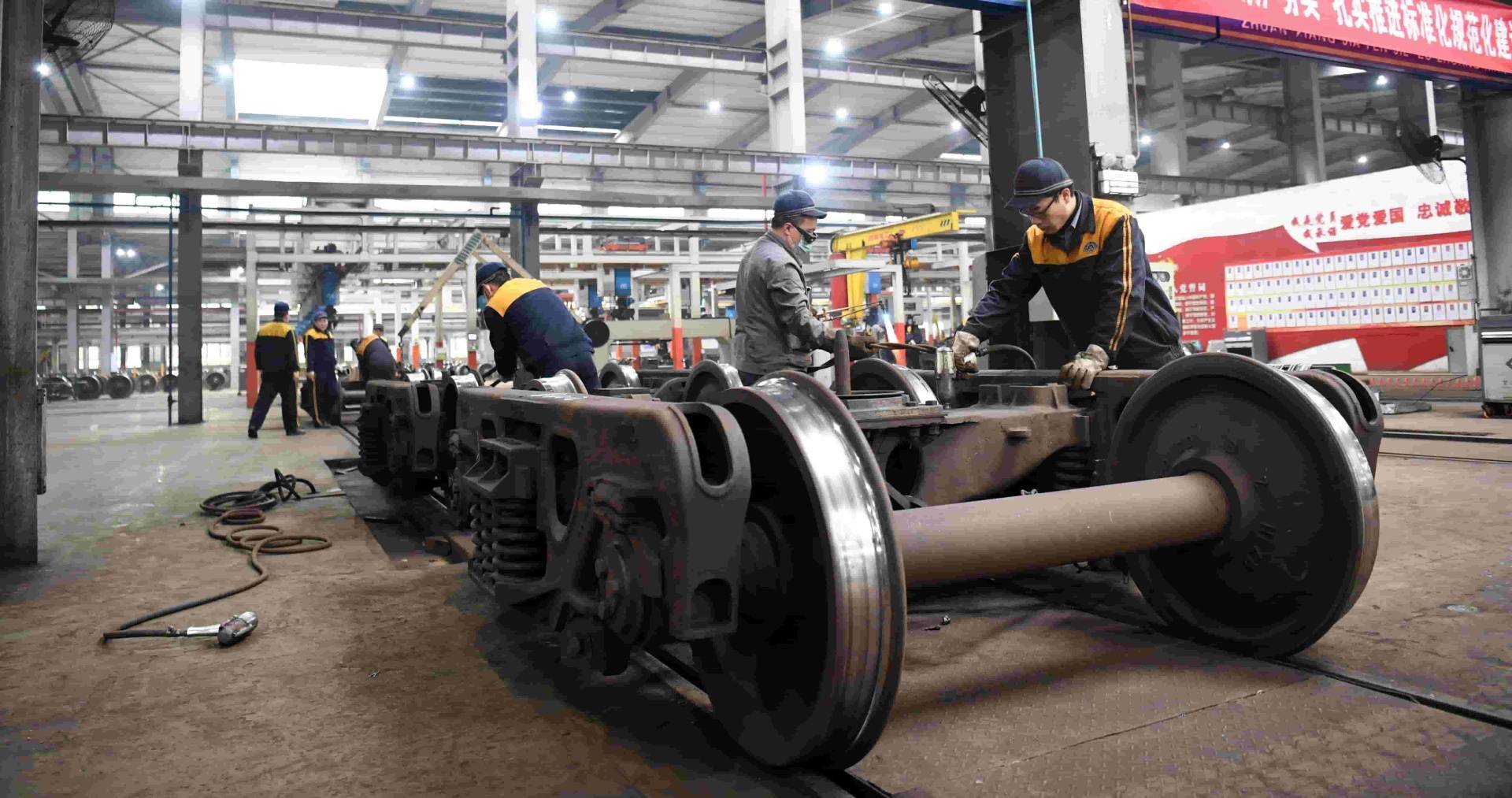
2. Steel for
wheels Wheels are the main load-bearing parts of vehicles and an important part of the running system of vehicles. Wheel and tyre steel is killed steel smelted by electric furnace or converter. According to the production process, it is divided into rolled steel wheels and cast steel wheels. Generally speaking, high-end wheels such as passenger cars and high-speed trains are usually produced by steel rolling process. For heavy-duty trains, the wheel-rail contact stress is large, especially under high stress, the area of the wheel-rail contact area is enlarged, and the wheels wear large when the train is running, which is prone to contact fatigue failure. Therefore, the steel for heavy-duty train wheels needs higher wear resistance and anti-fatigue performance, and at the same time, thermal fatigue damage resistance must be considered.
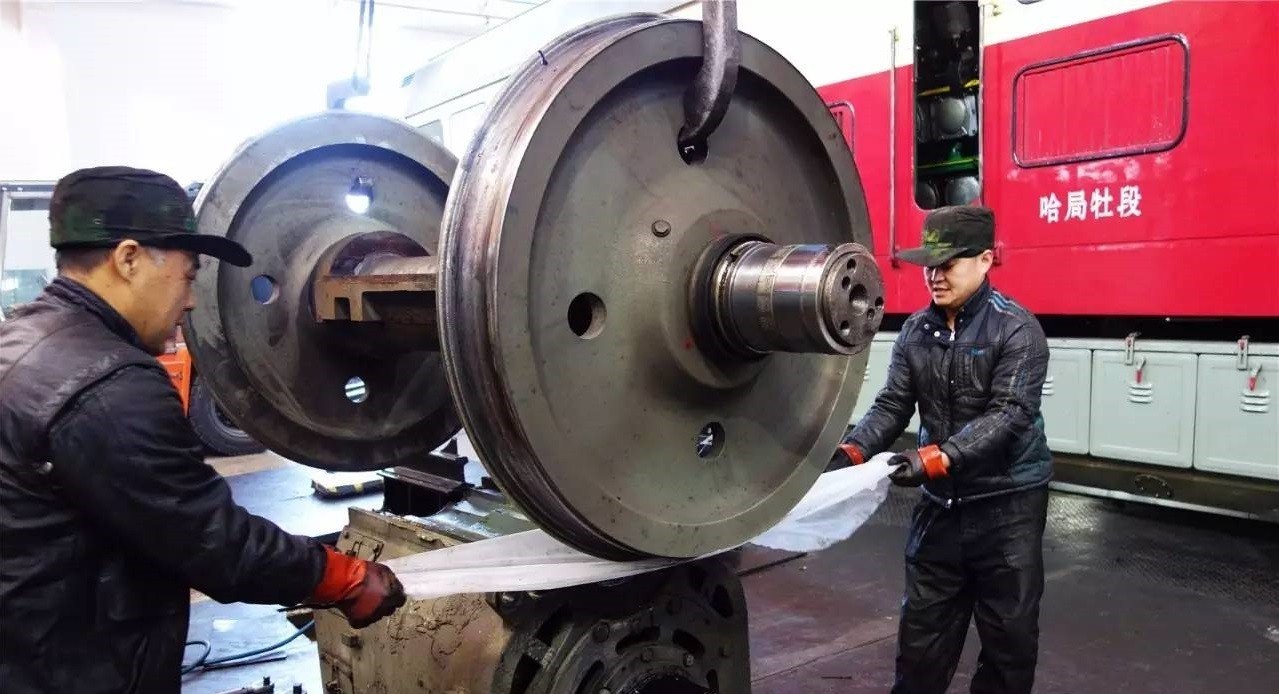

3. Steel for
axles The axle is an important part of railway locomotives and vehicles, and an important part of the running system of the vehicle. If the axle breaks, it will cause the train to derail. The axle steel should have good fatigue strength and impact resistance.

4. Steel for
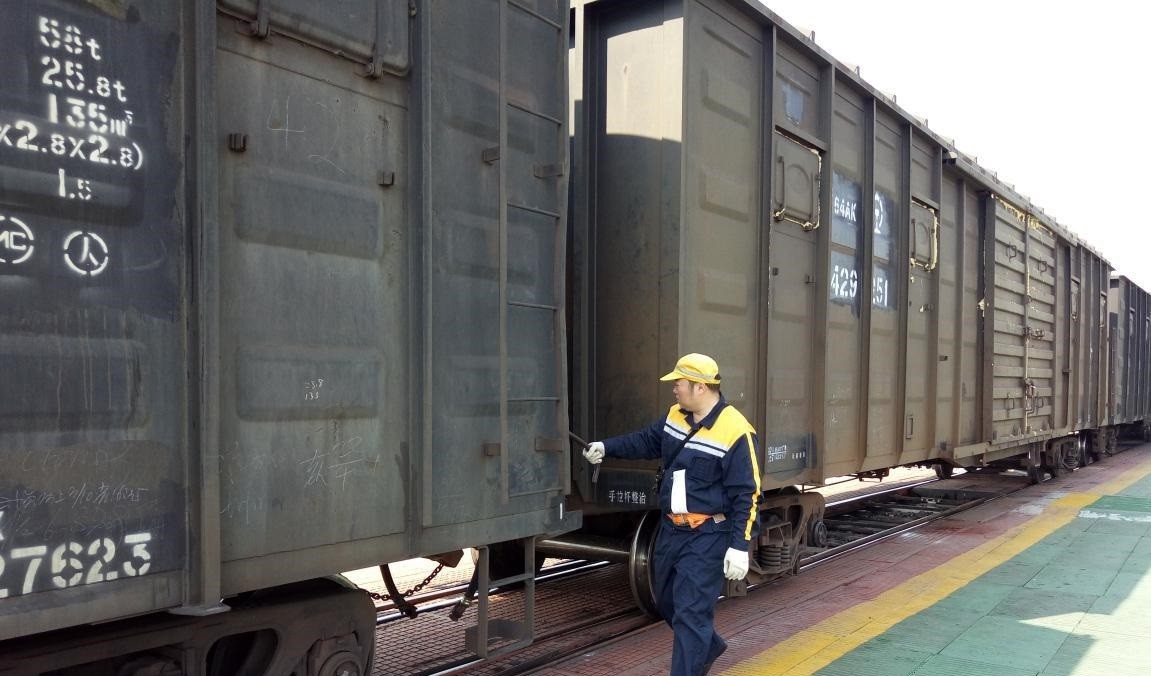
car body The steel for car body is mainly steel for the main beam of the car body, the frame, the inner and outer compartment plates, etc. The types of steel mainly include stainless steel, weathering steel, weathering steel, etc. The basic requirement is high strength and high corrosion resistance. , High weldability and lightweight. The steel used for railway freight cars is mainly high-strength weather-resistant and corrosion-resistant steel.

Personalized Information Service!
Drop your email to get market insights, product specs and latest rate info.
Copyright©2014-2025. BISCO. All Rights Reserved.
anything
Sitemap | Contact Us | Privacy Statement | Terms of Use | Online Security